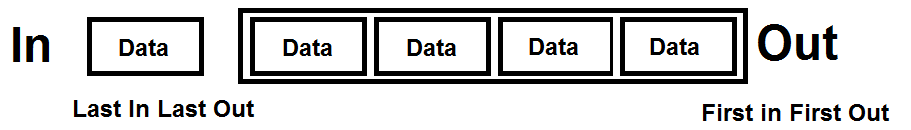
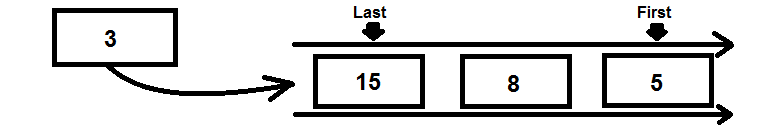
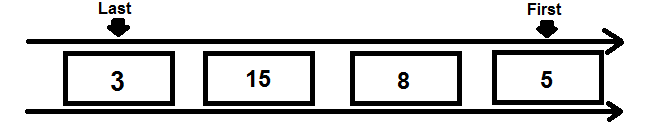
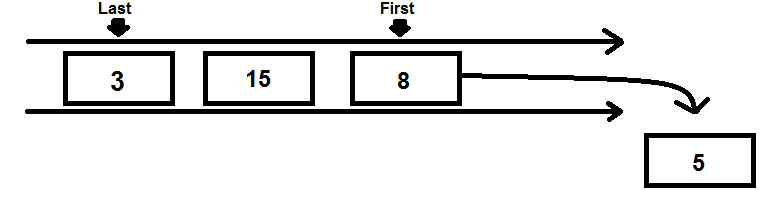
The queue data structure is similar to the stack, where there are restrictions on adding and removing elements. likewise, queue follows the first-in-first-out (FIFO) principle where the data item stored first will be accessed first.
Diagram of a Queue data structure
Operations of a Queue data structure
Enqueue – This will add an element to the queue
The steps of the Enqueue operation are:
- Check to see if the queue is full
- If it’s full, show an error message and end
- If the queue is not full, increment the last pointer to point to the next empty slot
- Add the data element where the queue location
Dequeue – This will remove an element in the queue
The steps of the Dequeue operation are:
- Check to see if the queue is empty
- If it’s empty, show an error message and end
- If the queue is not empty, access the element where the front is pointing
- Increment the front pointer to point to the next available data element
Functions to add which will make a queue more efficient
- isFull() – This will check to see if the queue is full
- isEmpty() – This will check to see if the queue is empty
- Peek() – Retrieve the element at the front of the queue without removing it
C++ Implementation of a circular queue
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Circular Queue using Arrays
// By Sahil Bora
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------
//---------------------------------------------
// Header files
//---------------------------------------------
#include <iostream>
#include <conio.h>
#include "queue.h"
using namespace std;
//----------------------------------------------------
// Queue class
// This can be used as a header file
// File:cqueue.h
//----------------------------------------------------
const int MAX = 5;
class cqueue
{
int a[MAX],front,rear;
public:
cqueue()
{
front = rear = ?1;
}
void insert(int);
int deletion();
void display();
};
//---------------------------------------------
// Queue insert constructor
//---------------------------------------------
void cqueue::insert(int val)
{
if((front==0 && rear==MAX?1) || (rear+1==front))
cout<<" Circular Queue is Full";
else
{
if(rear==MAX-1)
rear=0;
else
rear++;
a[rear]=val;
}
if(front==-1)
front=0;
}
//---------------------------------------------
// Queue deletion constructor
//---------------------------------------------
int cqueue :: deletion()
{
int k;
if(front==-1)
cout<<"Circular Queue is Empty";
else
{
k=a[front];
if(front==rear)
front=rear=-1;
else
{
if(front==MAX-1)
front=0;
else
front++;
}
}
return k;
}
//---------------------------------------------
// Queue display constructor
//---------------------------------------------
void cqueue :: display()
{
int i;
if(front==-1)
cout<<"Circular Queue is Empty";
else
{
if(rear < front)
{
for(i=front;i<=MAX?1;i++)
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
for(i=0;i<=rear;i++)
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
else
{
for(i=front;i<=rear;i++)
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
}
}
//--------------------------------------------------------
// Main Menu display code
//--------------------------------------------------------
void main()
{
cqueue c1;
int ch,val;
char op;
do
{
cout<<"CIRCULAR QUEUE IMPLEMENTATION IN C++\n";
cout<<"----------Menu----------\n";
cout<<"1.Insertion\n";
cout<<"2.Deletion\n";
cout<<"3.Display\n";
cout<<"4.Exit\n";
cout<<"Enter Your Choice <1..4> ?";
cin>>ch;
switch(ch)
{
case 1 : cout<<"Enter Element to Insert ?";
cin>>val;
c1.insert(val);
break;
case 2 : val=c1.deletion();
cout<<"Deleted Element :"<<val<<endl;
break;
case 3 : c1.display();
break;
}
cout<<"Do you want to continue<Y/N> ?";
cin>>op;
}
while(op=='Y' || op=='y');
getch();
}
Share this post